BB.AudioAnalyser
A module for doing FFT ( Fast Fourier Transform ) analysis on audio
Index
Constructor
BB.AudioAnalyser
(
-
config
)
-
config
Parameters:
-
configObjectA config object to initialize the Sampler, must contain a "context: AudioContext" property and can contain properties for fftSize, smoothing, maxDecibels and minDecibels ( see AnalyserNode for details )
Example:
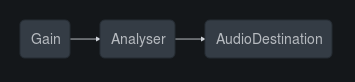
in the example bellow "samp" is assumed to be an instanceof BB.AudioSampler ( represented by the Gain in the image below ), it's connected to the Analyser which is connected to the BB.Audio.context ( ie. AudioDestination ) by default
BB.Audio.init();
var fft = new BB.AudioAnalyser();
// assuming samp is an instanceof BB.AudioSampler
samp.connect( fft );
// you can override fft's defaults by passing a config
var fft = new BB.AudioAnalyser({
context: BB.Audio.context[3],
connect: BB.Audio.context[3].destination
});
view basic BB.AudioAnalyser example
Properties
ctx
AudioContext
default:BB.Audio.context
the Audio Context this derived from
gain
GainNode
private
the "output" gain node ( use .volume, .setGain() to interface with this )
node
AnalyserNode
the AnalyserNode itself
volume
Number
default:1
the master volume (of output gain node)
Methods
connect
(
-
destination
-
output
-
input
)
-
destination -
output -
input
connects the Noise to a particular AudioNode or AudioDestinationNode
Parameters:
-
destinationAudioNodethe AudioNode or AudioDestinationNode to connect to
-
outputNumberwhich output of the the Noise do you want to connect to the destination
-
inputNumberwhich input of the destination you want to connect the Noise to
Example:
BB.Audio.init();
var node = new BB.AudioBase({
volume: 0.75,
});
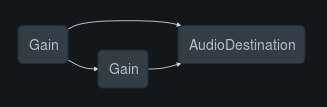
node.connect( exampleNode );
// connected to both default BB.Audio.context && exampleNode
// so if exampleNode is also connected to BB.Audio.context by default,
// ...then you've got node connected to BB.Audio.context twice
...which looks like this ( where the first Gain is the Noise and the second is the exampleNode )
disconnect
(
-
destination
-
output
-
input
)
-
destination -
output -
input
diconnects the Noise from the node it's connected to
Parameters:
-
destinationAudioNodewhat it's connected to
-
outputNumberthe particular output number
-
inputNumberthe particular input number
BB.Audio.init();
var node = new BB.AudioBase({
volume: 0.75,
});
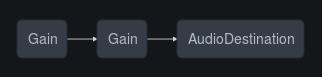
node.disconnect(); // disconnected from default BB.Audio.context
node.connect( exampleNode ); // connected to exampleNode only
...which looks like this ( where the first Gain is the node and the second is the exampleNode )
getAmplitude
()
returns the averaged amplitude between both channels
getByteFrequencyData
()
returns an array with frequency byte data
Example:
BB.Audio.init();
var fft = new BB.AudioAnalyser();
// then in a canvas draw loop...
var fdata = fft.getByteFrequencyData();
for (var i = 0; i < fdata.length; i++) {
var value = fdata[i];
var percent = value / 256;
var height = HEIGHT percent;
var offset = HEIGHT - height - 1;
var barWidth = WIDTH/fdata.length;
ctx.fillRect(i barWidth, offset, barWidth, height);
};
getByteTimeDomainData
()
returns an array with time domain byte data
Example:
BB.Audio.init();
var fft = new BB.AudioAnalyser();
// then in a canvas draw loop...
var tdata = fft.getByteTimeDomainData();
ctx.beginPath();
var sliceWidth = WIDTH / tdata.length;
var x = 0;
for (var i = 0; i < tdata.length; i++) {
var v = tdata[i] / 128.0;
var y = v * HEIGHT/2;
if(i===0) ctx.moveTo(x,y);
else ctx.lineTo(x,y);
x+=sliceWidth;
}
ctx.lineTo(WIDTH,HEIGHT/2);
ctx.stroke();
getFloatFrequencyData
()
returns an array with frequency float data
getFloatTimeDomainData
()
returns an array with time domain float data
getPitch
()
Number
returns pitch frequency (float) in Hz, based on Chris Wilson
Returns: Number
pitch
getResampledBufferData
()
returns an multi-dimentional array ( one array per channel ) with resampled buffer data ( for drawing an entire waveform of a file )
Example:
BB.Audio.init();
var fft = new BB.AudioAnalyser();
// then in a canvas draw loop...
var tdata = fft.getResampledBufferData();
ctx.beginPath();
var sliceWidth = WIDTH / tdata.length;
var x = 0;
for (var i = 0; i < tdata.length; i++) {
var v = tdata[i] / 128.0;
var y = v * HEIGHT/2;
if(i===0) ctx.moveTo(x,y);
else ctx.lineTo(x,y);
x+=sliceWidth;
}
ctx.lineTo(WIDTH,HEIGHT/2);
ctx.stroke();
setGain
(
-
num
-
ramp
)
-
num -
ramp
sets the gain level of the node ( in a sense, master volume control )
Parameters:
-
numNumbera float value, 1 being the default volume, below 1 decreses the volume, above one pushes the gain
-
rampNumbervalue in seconds for how quickly/slowly to ramp to the new value (num) specified
Example:
BB.Audio.init();
var node = new BB.AudioBase({
volume: 0.75
});
node.setGain( 0.25, 2 ); // lower's volume from 0.75 to 0.25 in 2 seconds
// if no ramp value is needed, you could alternatively do
node.volume = 0.5; // immediately jumps from 0.25 to 0.5